-
Gallery of Images:
-
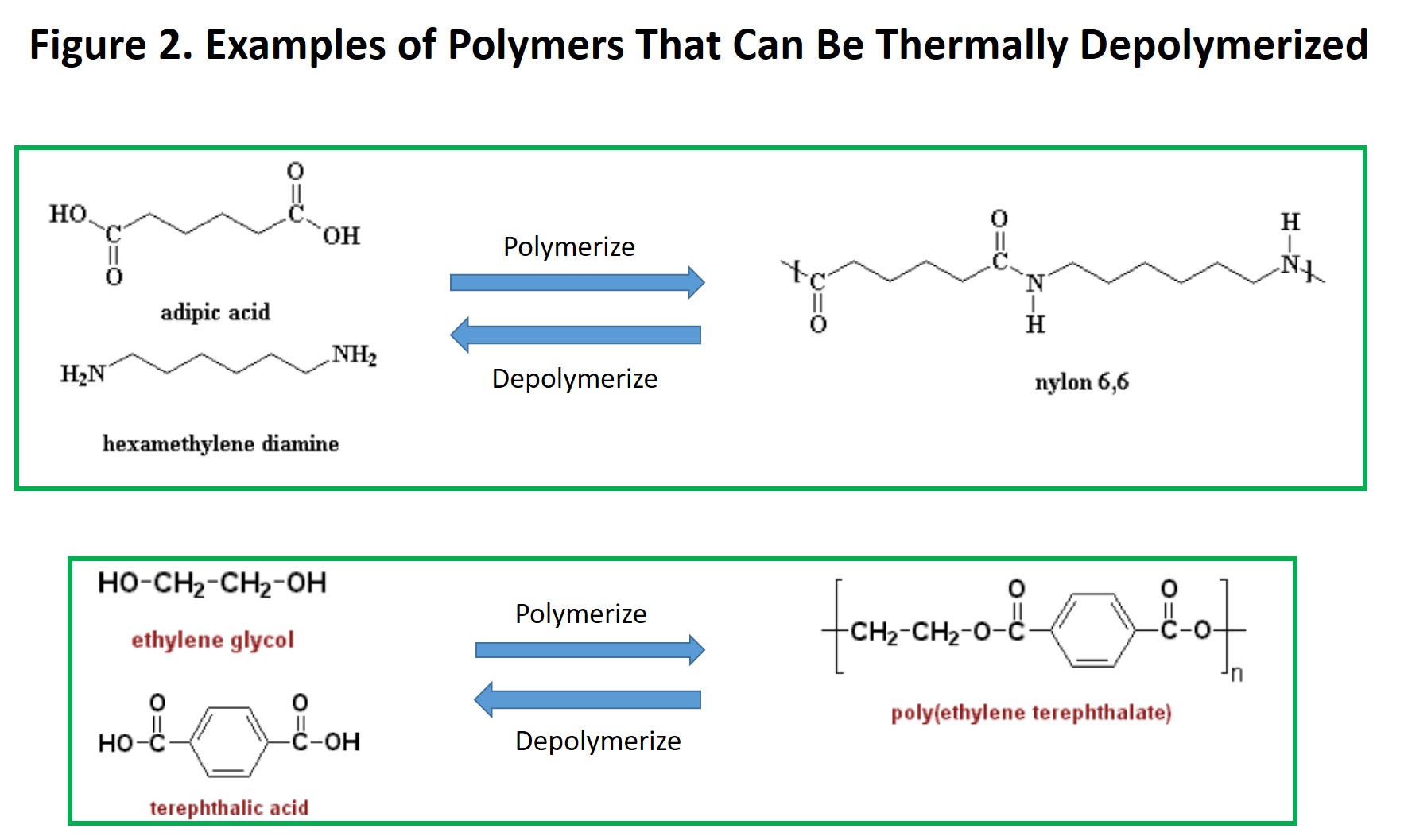
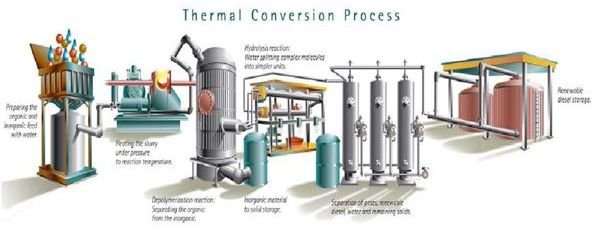
Depolymerization (or depolymerisation) is the process of converting a polymer into a monomer or a mixture of monomers. All polymers depolymerize at high. This paper reviews ways that biomass can be converted by thermal depolymerization to make synthetic gas, i. Biomass, being carbon neutral, is considered as a form of solar energy stored during the growing season by photosynthesis. Alternatively, there is an attractive process for recycling by thermal or catalytic method which produces hydrocarbon. The pyrolysis can be cost effective compared to other processes. The pyrolysis thermally degrades the plastic component to produce an oil and gas product. US A1 Lactide Production from Thermal Depolymerization of PLA with applications to Production of PLA or other bioproducts Google Patents the present invention provides a method for the production of lactide directly from recycled PLA wastes using thermal depolymerization process. Thermal depolymerization (TDP) is a depolymerization process using hydrous pyrolysis for the reduction of complex organic materials (usually waste products. Study of Thermal Depolymerization Process 359 Figure 2. Integral intensity I to I at T 295 K ratio vs. 1T of PC1 and PC2 of the C 60 phases in vacuum (empty symbols) and in air (black symbols). Thermal depolymerization is the processes of raising and lowering the heat and pressure of something so that the long molecular chains of hydro carbons are broken down. This process has been previously attempted by scientists with patents going all the way back to the 1970s. Thermal depolymerization is a process that involves creating oil from organic materials such as plastic and animal waste. The first step of TDP takes plastics or organic waste and grinds them up with water. This mixture, also called the feedstock, is heated to between 200 and 300 The thermal depolymerization process is not, of course, 100 percent efficient. This implies, even in a bestcase scenario of high efficiency and widespread deployment, continued utilization of energy from outside the loop, so to speak. Thermal depolymerization (TDP) is a depolymerization process using hydrous pyrolysis for the reduction of complex organic materials (usually waste products of various sorts, often biomass and plastic) into light crude oil. It mimics the natural geological processes thought. Thermal depolymerization (TDP) is a process for the reduction of complex organic materials (usually waste products of various sorts, often known as biomass) into light crude oil. Thermal depolymerization (TDP) is a process for the reduction of complex organic materials (usually waste products of various sorts, often known as biomass and plastic) into light crude oil. It mimics the natural geological processes thought to be involved in the production of fossil fuels. Thermal Depolymerization quote: Unlike other solidtoliquidfuel processes such as cornstarch into ethanol, this one will accept almost any carbonbased feedstock. Thermal depolymerization is within the scope of WikiProject Polymers which aims to improve the coverage of polymerrelated articles in Wikipedia. If you are interested, you may visit the project page and join with us. Feel free to leave messages at the project talk page. Thermal Depolymerization seems to be one such process that I've been telling people about for years. I first heard about TDP around 2004 (that's the date on the UTube video, by the way), and have never been able to understand why it hasn't been siezed on. Thermal depolymerization (TDP) is a process for the reduction of complex organic materials (usually waste products of various sorts, often known as biomass) into light crude oil. It mimics the natural geological processes thought to be involved in the production of fossil fuels. Thermal Depolymerization Pro to the Con: Miranda Hurtado Taylor Mosier a process of breaking down complex hydrocarbons in an oxygendeprived, heated and pressurized environment to yield simpler compounds that can be used to produce fuels. Thermal depolymerization (TDP) is a depolymerization process using hydrous pyrolysis for the reduction of complex organic materials (usually waste products of various sorts, often biomass and. Whatever happened to that thermal depolymerization process, where scrap turkey guts, etc. , were being turned into oil and other stuff? Several years ago I think I read that a pilot plant was being built that was (IIRC) technically successful but ran into problems with smelly emissions. with that in the thermal (noncatalytic) run. Amon the catalysts examined, the order of The process is easily controllable for preferential formation of gasolinerange hydrocarbons. Production of the latter can be rationalized in terms of stepwise breakdown of the polymeric chains by a carbonium ion mechanism. What Is Thermal Depolymerization? Thermal Depolymerization is the conversion of assorted plastics in petroleum, or fuel for vehicles. It uses heat and water to break down the polymer chains of many different plastics and other mixtures in order to create the liquid we see at gas and service stations. Process, LLC owns and operates demonstration facility for the Thermal Depolymerization Process (TDP) technology. The company was founded in 1998 and is based in. Thermal depolymerization machines turbocharge the process by precisely raising heat and pressure to levels that break the feedstock's long molecular bonds. Many scientists have tried to convert organic solids to liquid fuel using waste products before, but their efforts have been notoriously inefficient. Thermal depolymerization at the molecular level. The process of converting The waste plastics are fed into the extruder. The reactor places the long chain carbons under high pressure and allows the condensable vapor to pass into the condensation. The system diverts the noncondensable synthetic gas back into the furnaces to heat the. What is shorthand of Thermal Depolymerization Process? The most common shorthand of Thermal Depolymerization Process is TDP. You can also look at abbreviations and acronyms with word TDP in. During the initial stages of thermal depolymerization of PHBV, the low molecular weight PHBV and PHBV with crotonate end group at the terminal are generated by chain scission process. Meanwhile, the depolymerization of PHBV macromolecular can be accelerated by residues Ca ions. To clarify the reaction mechanism of PET depolymerization in supercritical methanol is important applying it to commercial recycle process. We have reported the continuous kinetics analysis for PET depolymerization in supercritical Thermal depolymerization is an industrial process of breaking down various waste materials into crude oil products. In this process, the materials are subjected to high temperatures and pressure in the presence of water, thereby initiating hydrous pyrolysis. Hydrous thermal depolymerization (HTD) is an aqueous temperature and pressure regulated process that's used to break down long hydrocarbon polymers found in organic matter into various products, including crude oil. process of polymer chain decomposition till monomers or oligomers which undergo at high temperature or hydrolytic agents. So, there are distinguishing thermal and chemical depolymerization suitable. Commonly, as thermal depolymerization is classified chemical reaction in which polymer chain converses to monomer at high temperature. Thermal depolymerization (TDP) is a process using hydrous pyrolysis for the reduction of complex organic materials (usually waste products of various sorts, often known as. All content on this website, including dictionary, thesaurus, literature, geography, and other reference data is for informational purposes only. Thermal Depolymerization freestylejunki32. Loading Unsubscribe from freestylejunki32? fuel from waste plastic PYROLYSIS PROCESS IN PLASTICS. Depolymerization (or depolymerisation) is the process of converting a polymer into a monomer or a mixture of monomers. This process is driven by an increase in entropy. Modifications were then made to the process, and production was increased to 50 percent, then 75 percent, with modifications at each step. Lately, the RES plant has been operating at 100 percent of capacity, and once again, modifications are being made to the thermal depolymerization process that converts materials from the Butterball plant. Changing World Technologies (CWT)'s Thermal Conversion Process purportedly reforms organic waste into renewable fuel oil, without combustion, incineration or toxic residue, providing a solution for solid waste management while creating a renewable domestic source of energy. Thermal depolymerization is an industrial process for breaking down various waste materials into crude oil products. This involves subjecting the materials to high temperatures and pressure in the presence of water, thereby initiating a process known as hydrous pyrolysis. It was a look at a technology called thermal depolymerization (TDP), which could take any organic material and turn it into oil. This was a high profile writeup with a lot of hype, and the technology of Brian Appel and his company Changing World Technologies (CWT) was really Thermal depolymerization ( TDP ) is a depolymerization process using hydrous pyrolysis for the reduction of complex organic materials (usually waste products of various sorts, often biomass and plastic ) into light crude oil. [0015 A process for the depolymerization of acrylic polymers via catalytic pyrolysis is revealed in the document PI, more specifically depolymerization of acrylic polymers via catalytic pyrolysis of acrylic acid monomer esters replaced or not, from a polymeric material. This process is known as unzipping, depropagation or endchain depolymerization. Random main chain scission, on the other hand, leads to the formation of both monomers and oligomers (short chains with ten or fewer monomers). Thermal depolymerization is a process wherein depolymerization takes place with the help of hydrous pyrolysis in order to reduce complex organic materials into light crude oil. Pyrolysis is nothing but the decomposition of any organic substance with no oxygen present. The thermal depolymerization process (TDP)is quietly brewing new hope for sustainably dealing with the massive waste stream produced by the activities of mankind. Thermal depolymerization (TDP) is a process for the reduction of complex organic materials (usually waste products of various sorts, often known as biomass and plastic) into light crude oil. It mimics the natural geological processes thought to be involved in the production of fossil fuels. Thermal depolymerization (TDP) is a depolymerization process using hydrous pyrolysis for the reduction of complex organic materials (usually waste products of various sorts, often biomass and plastic) into light crude oil and methane gas. It mimics the natural geological processes thought to be involved in the production of fossil fuels. Thermal depolymerization differs in that it contains a hydrous process followed by an anhydrous cracking distillation process, although upgrading of the raw HTU product is also possible. History Thermal depolymerization is similar to the geological processes that produced the fossil fuels used today, except that the technological process. The thermal depolymerization plant built nearby is a joint venture of ConAgra and Changing World Technologies (CWT) of West Hempstead, New York. Estimates are that the plant can convert the waste into 500 barrels (21, 000 US gallons) of oil daily. Answers about thermal depolymerization. Thermal depolymerization is a heatdriven process that breaks down or transforms polymers into the shorter chains from whence they came: oil. The depolymerization of lignin polymer into its lower molecularweight oligomers and monomers is a remarkable approach to generate bulk chemicals and biofuels. However, the use of lignin as a precursor for the synthesis of polymeric materials is difficult..
-
Related Images: