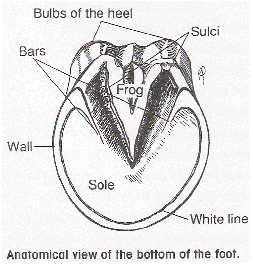
-
Gallery of Images:

-
Urine gives valuable information to the veterinary practitioner regarding kidney function and other urinary system abnormalities such as crystals, casts and infections. NonMammalian Renal Systems The renal anatomy and physiology of fish, amphibians, birds and reptiles is significantly different to that of mammals. Equine Temporomandibular Joints (TMJ): Morphology, Function, and Clinical Disease Gordon J. Baker, BVSc, PhD, MRCVS, Diplomate ACVS TMJ are complex but well designed fulcra that leverage the masticatory power of muscles and dental Equine Anatomy A Guided Tour of Equine Anatomy is a dissection Veterinary Technicians (OAVT) and Equestrian Canada. For more information contact Equine Guelph ext email: horses@uoguelph. ca Register highlighting form and function. A Guided Tour of Equine Anatomy is a dissection workshop to understand equine anatomy first hand. Participants will have an opportunity to take part in a guided examination of the anatomy of a horse. An overview of the large muscle groups of the neck, trunk and legs is followed by an exploration of the abdomen and chest. Veterinary Anatomy And Veterinary Physiology Welcome to the Anatomy and Physiology section of WikiVet. Anatomy is the study of form and structure of organisms, whilst physiology is the study of the function of an organism and the processes, physical, chemical and biological, occuring within it. Cat Anatomy Notice that the kidneys are not labeled on this picture. The kidneys are tucked up close to the liver toward the spine. Image modified from Hill's Pet. Where: Ontario Veterinary College Cost: 280 before Mar 30, 2014 300 after Advanced Equine Anatomy is offered following the Guided Tour of Equine Anatomy workshop and continues the handson investigation of the anatomy of the horse. highlighting form and function. In addition to the sensory information processed by the special senses of sight, smell and hearing, the cranial nerves supply additional sensory information from all parts of the head (Figs 4 and 5). This anatomical veterinary illustration of the equine stifle joint anatomy with the patella in the locked position was created to be utilized within a powerpoint presentation for equine veterinary students who were studying various gait abnormalities in the hind limb of the horse. Veterinary medicine is the branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of disease, disorder and injury in nonhuman animals. The scope of veterinary medicine is wide, covering all animal species, both domesticated and wild, with a wide range of conditions which can affect different species. Veterinary Equine Anatomy: Form and Function is a unique text that presents the essentials of equine anatomy in a systemic and regional approach. Fully illustrated in vivid, four color throughout, the text provides clinically relevant information on the fundamental anatomy required by the student or veterinarian in an Equine or mixed practice. Anatomy of the Dog: An Illustrated Text, Fifth Edition, A revised edition of this superbly illustrated atlas with a new section on computed include colour line diagrams, radiographs, ultrasound and CT scans providing the reader with detailed information on the structure and function of all the body systems and their interaction in the living animal. The purpose of this article is to discuss normal form and function as they may relate to the clinical process. By necessity, function must be induced from observation of the form of a structure and observation of the structure in action, the process of reverse engineering. Functional anatomy of the equine interphalangeal. Jeff is the Anatomy Professor with Biomedical Sciences at the University of Guelph. The majority of his time is spent teaching equine anatomy to the veterinary students at the Ontario Veterinary College and carrying out his internationally recognized research. Kirstie Dacre, BVMS, MSc, Cert EM (Int Med), PhD. bit causing osseous sequestra or spurs to form. 2 In the young horse, the ventral border of the mandible is wide and round, but as the horse ages, and eruption of the mandibular. Well known for his ability to bring anatomy to life, Dr. Thomason teaches anatomy to veterinary students at the Ontario Veterinary College. Thomason is a researcher conducting internationally recognized research on the equine hoof. Thomason will be your guide through basic to more advanced anatomy topics highlighting form and function. Buy Veterinary Equine Anatomy: Form and Function Illustrated edition by Jerome Masty (ISBN: ) from Amazon's Book Store. Everyday low prices and free delivery on eligible orders. Form and function of the equine digit Andrew Parks, VetMB, MS, MRCVS Department of Large Animal Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Georgia, 501 DW Brooks Drive, Athens, GA, USA An anatomy course is required for the Equinology Equine Body Worker Level II certification. A second anatomy course is required for the Equinology Master Equine Body Worker certification. Students may take EQ200, EQ900 or EQ910 to fulfill these requirements. Form and function of the equine digit Parks, Andrew 00: 00: 00 There are many reasons why an equine clinician should have a thorough understanding of the anatomy and physiology of the equine digit. Palpation skills, perineural and intraarticular anesthesia, and surgery all. This first article of a 12part series on equine anatomy and physiology discusses basic terminology, the horses largest means in the realm of form to function. We will not be quoting a lot of sources, for the most part, because the information to be Equine Veterinary Technicians and Enjoy These Benefits. Virtual Canine Anatomy is an innovative anatomy program that has received outstanding accolades from members of the American Association of Veterinary Anatomists, students, and instructors both in the United States and internationally. This course is designed to give the basic understanding of equine anatomy and normal physiology. Special attention will be given to understanding form versus function when discussing each lesson. Each lesson will be designed around a system approach with discussion of the anatomy of a body system. Histological characteristics of healthy equine temporomandibular joints (TMJs) were determined. Articular surfaces of the equine TMJ are coated with fibrocartilage. Wi Equine anatomy refers to the gross and microscopic anatomy of horses and other equids, including donkeys, and zebras. While all anatomical features of equids are described in the same terms as for other animals by the International Committee on Veterinary Gross Anatomical Nomenclature in the book Nomina Anatomica Veterinaria, there are many horsespecific colloquial terms used by equestrians An understanding of equine specific external and internal anatomy including medical and layman terms is an important part of a veterinary assistant or technicians role in practice. Correct use of terminology in the veterinary workplace enhances client education and practicewide communication. The Department's mission is to emphasize programs with a strong correlation between structure and function and to focus on integration of cellular and molecular biology with the biology of cell populations organized as tissues, organs, organ systems and organisms. This video shows the flight biomechanics of the horse leg, specifically Icelandic Horses, and shows several deviations, such as winging in and rope walking Instructor: Dr. Jeff Thomason is the Anatomy Professor with Biomedical Sciences. The majority of his time is spent teaching anatomy to the veterinary students at the Ontario Veterinary College and carrying out his internationally recognized research on the form and function of. Equine Distal Limb Stunning full color anatomy photos that reveal the form and function of the distal limb structures Find this Pin and more on From Anatomy of the Equine by Animated Horse. The suspensory ligament plays a vital role in stabilizing the equine distal limb. The Online Veterinary Anatomy Museum (OVAM) project was funded by JISC as part of the Content Programme. It aims to provide access to veterinary anatomical resources in. ACPAT Veterinary Physiotherapists are professional clinicians with a depth of core knowledge that includes anatomy and physiology, joint mechanics, functional biomechanics, disease pathophysiology and tissue healing. The Gonads and Genital Tract of Horses: Reproductive Disorders of Horses: The Merck Manual for Pet Health AG 313 Kenzie Find this Pin and more on Equine System: Reproductive Sexual by Joy Koritz. Learn about the veterinary topic of The Gonads and Genital Tract of Horses. Encuentra Veterinary Equine Anatomy: Form and Function de Jerome Masty (ISBN: ) en Amazon. Form meets function in a horse with good conformation. Learn equine anatomy terms by visiting the Equine Anatomy Project. About the Author Diagnosing Horse Lameness The Veterinary Process. Prevent Lameness in Your Horse. Basic Hoof and Leg Protection for the Sport Horse. Students interested in the structure and function of the horse, including riders, trainers, farriers, veterinary technicians, Equine massage therapists and other health care practitioners, coaches, photographers, artists and others. Equine Anatomy: Understanding Anatomy is the cornerstone to practicing Equine Massage Therapy. This course is designed to give the student thorough knowledge of the functions of the skeletal, muscular, circulatory, and nervous systems. CVM 6100 Veterinary Gross Anatomy General Anatomy Carnivore Anatomy Lecture Notes by selectively thickened to form ligaments NOTE: Joint Capsule fibrous layer and synovial membrane together. since force is a function of cross sectional area a pennated muscle can generate more. Review Article Equine dental and periodontal anatomy: A tutorial review C. Pschke Institute of Veterinary Anatomy, Histology and Embryology, Faculty of Veterinary. Equine Skeletal Anatomy Horse Bones Structure and Function If you can understand equine skeletal anatomy, you'll have a good grasp on the framework of how the horse's body is built. Our equine friends have about 205 bones in their body that provide structure, give rise to joints to allow for movement, and offer protection to vital organs. Reviewing equine anatomy, neurology, and physiology, but With a different outlook! Then, we can discuss the implications of this Equine Form and Function The Biomechanics of Movement, With Emphasis on the Spine and Pelvis Author: Dennis Eschbach Created Date. The Online Veterinary Anatomy Museum (OVAM) project was funded by JISC as part of the Content Programme. It aims to provide access to veterinary anatomical resources in. Designed For: Students interested in the structure and function of the horse, including riders, trainers, farriers, veterinary technicians, Equine massage therapists, and other healthcare practitioners, coaches, photographers, artists, and others NOTE: This course is a core course in the Equine Science Certificate and Diploma in Equine Studies. Define anatomy Discuss the TISSUE Groups of cells with same general function e. , muscle, nerve CELL Smallest unit of protoplasm ORGAN SYSTEM Several organs e. , respiratory, digestive, reproductive systems CELL Form the junction between two or more bones. Functional anatomy and biomechanics of the equine thoracolumbar spine: a review Hafsa ZANEB 1, , Christian PEHAM 2, Christian STANEK 2 1 Department of Anatomy and Histology, University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Lahore, Pakistan RVC Equine. 6, 564 likes 61 talking about this 366 were here. RVC Equine Hospital and Equine Practice she is now back to normal and in winning form! RVC's Senior Lecturer in Equine Medicine, Bettina Dunkel commented: RVC Equine Royal Veterinary College, RVC. The RVC's Equine Referral Hospital is in the unique position to offer. To understand how lameness occurs, you must be familiar with healthy joint function and how inflammation causes damage to the joint. Equine anatomy Archives Custom and stock veterinary, medical and scientific illustrations by Wendy Chadbourne, CMI, MFA Full color poster includes three illustrations of the. Veterinary Developmental Anatomy (Veterinary Embryology) CVM 6903 by Thomas F. Fletcher, DVM, PhD and Alvin F. 2, during which organs grow and begin to function. Fertilization: union of a haploid oocyte and a haploid spermatozoon, producing a diploid zygote outer blastomeres become flattened and form tight.
-
Related Images: