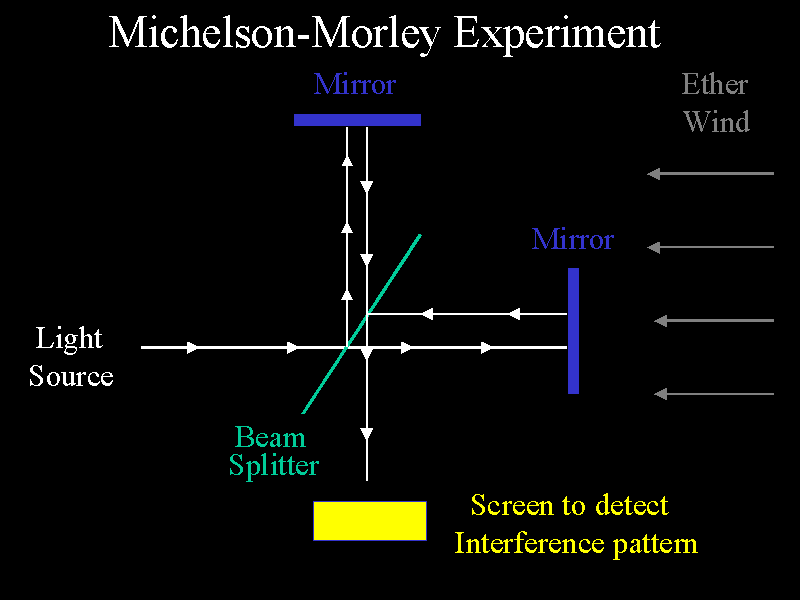
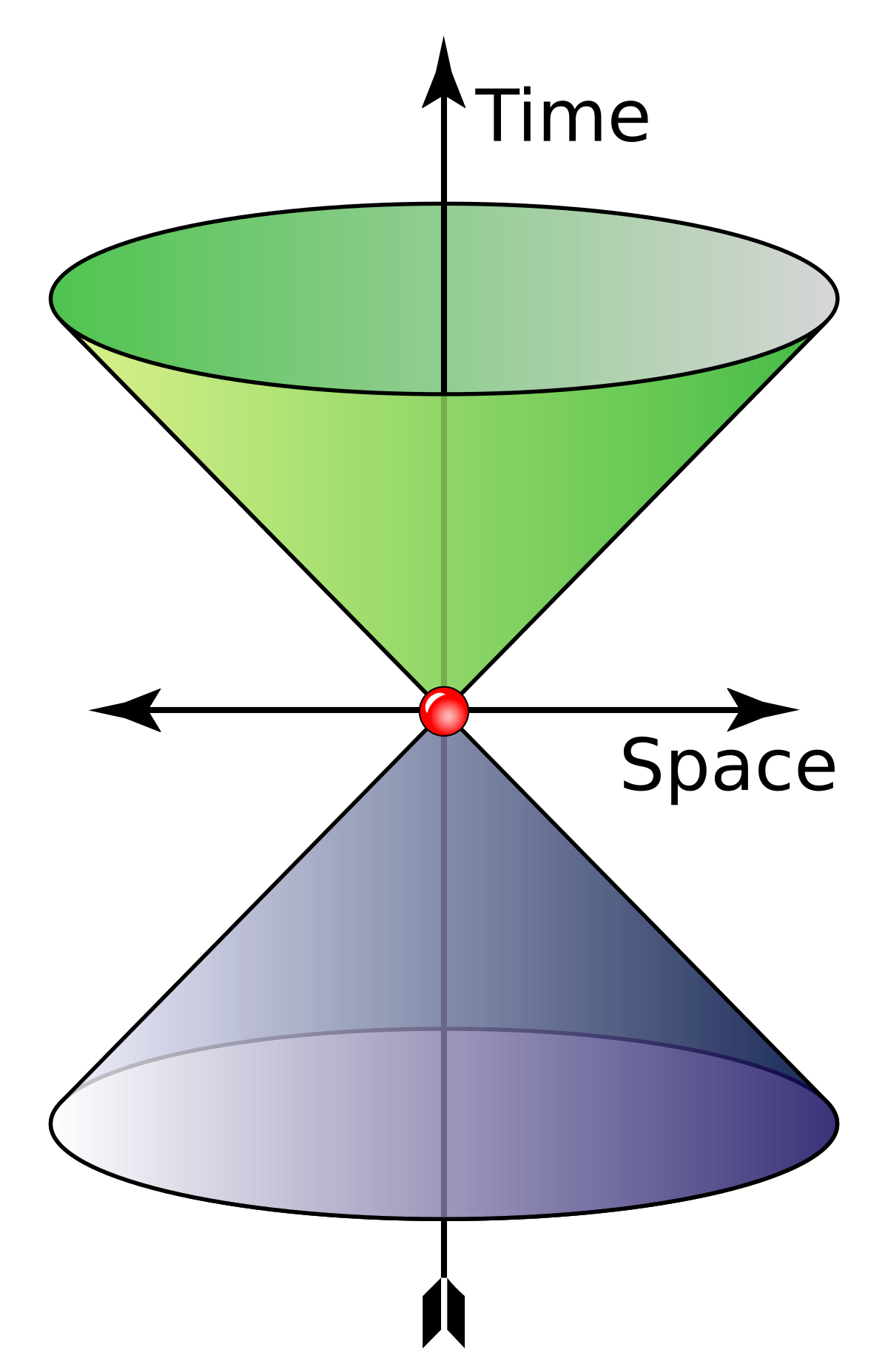
-
Gallery of Images:

-
Special relativity is a very important physics theory introduced by Albert Einstein in 1905 (his 'miracle year'). At the time it completely revolutionised our understanding of space and time. Special relativity is a theory proposed by Albert Einstein that describes the propagation of matter and light at high speeds. It was invented to explain the observed behavior of electric and fields, which it beautifully reconciles into a single socalled field, and also to. relativity the special and general theory by albert einstein, ph. professor of physics in the university of berlin translated by Einstein put forth special relativity, which explains motion at nearlight speeds. Although there are many consequences of Special Relativity, this complex theory consists of only two postulates. Understanding Einstein: The Special Theory of Relativity from Stanford University. In this course we will seek to understand Einstein, especially focusing on the special theory of relativity that Albert Einstein, as a twentysix year old patent. The book opens with a description of the smooth transition from Newtonian to Einsteinian behaviour from electrons as their energy is progressively increased, and this leads directly to the relativistic expressions for mass, momentum and energy of a particle. Einstein's theory of relativity is a famous theory, but it's little understood. The theory of relativity refers to two different elements of the same theory: general relativity and special relativity. The theory of special relativity was introduced first and was later considered to be a special. Special relativity (or the special theory of relativity) is a theory in physics that was developed and explained by Albert Einstein in 1905. It applies to all physical phenomena, so long as gravitation is not significant. Special relativity applies to Minkowski space, or flat spacetime (phenomena which are not influenced by gravitation). Einstein knew that some weaknesses had been. The theory of special relativity explains how space and time are linked for objects that are moving at a consistent speed in a straight line. One of its most famous aspects concerns objects moving. Introduction The Special Theory of Relativity was the result of developments in physics at the end of the nineteenth century and the beginning of the twentieth century. This original handwritten page from a 1912 manuscript of Einstein's Theory of Special Relativity shows a version of the famous equation Emc. Special relativity is the science of describing physics from the perspective of observers who do not accelerate. The basic principle is that for all these observers, the laws of physics should be the same, regardless of their velocity. The first halfhour episode of SPECIAL RELATIVITY premiered April 15, 2015 at and your favorite podcast provider. Special Relativity is all sound and comedy, evocative scenes and memorable characters. It's a fact of life: Some things are absolute, and some are relative. For me, the teapot on the table is to the left of my cup. From the point of view of an observer sitting directly opposite, it's the other way around: My cup is to the left of the teapot. Chapter 6 The Special Theory of Relativity 6. 1 Introduction The puzzling properties of light and the ether remained through the turn of the century and up to 1904: the. Think you know about time and space? Einstein basically did a pile driver on all our brains when he came up with his theory of special relativity. As a precursor to Einstein's Special Relativity Theory Maxwell had, a century earlier, established that light was an interaction between moving electricity and. Einstein's theory of general relativity predicted that the spacetime around Earth would be not only warped but also twisted by the planet's rotation. Gravity Probe B showed this to be correct. Special relativity, part of the wideranging physical theory of relativity formed by the Germanborn physicist Albert Einstein. It was conceived by Einstein in 1905. Along with quantum mechanics, relativity is central to modern physics. Special relativity is limited to objects that are moving with respect to inertial frames of referencei. , in a state of uniform motion with respect to one. Relativity provides eDiscovery software solutions that give corporations, governments, law firms tools to manage litigation, investigations FOIA requests. Learn about Relativity's eDiscovery solutions to aid legal review, litigation support, document management much more. Relativity: Einstein's theory of special relativity in multimedia tutorial. The introductory level takes 10 minutes, but has links to over 40 explanatory pages giving greater depth and detail. Einstein Light has a simple introduction to Galilean relativity, and their incompatibility; it explains how Einstein's relativity resolves this problem, and develops time dilation. In this course we will seek to understand Einstein, especially focusing on the special theory of relativity that Albert Einstein, as a twentysix year old. This is an essay about the special theory of relativity, illustrated with animations. The purpose is to deepen the reader's understanding. In 1905, Albert Einstein published the theory of special relativity, which explains how to interpret motion between different inertial frames of reference that is, places that are moving at constant speeds relative to each other. Einstein explained that when two objects are moving at a constant. either of two theories developed by Albert Einstein, the special theory of relativity, which requires that the laws of physics shall be the same as seen by any two different observers in uniform relative motion, and the general theory of relativity which considers observers with relative acceleration and leads to a theory of gravitation. ExpoScience IndustrySpacetime Wrinkles Forward Back Up Map Glossary Information What's So Special About Relativity? Einstein's first theory of relativity, which he published in 1905, broke away from the Newtonian reliance on space and time as immutable frames of reference. The Special Theory of Relativity is a theory of classical physics that was developed at the end of the nineteenth century and the beginning of the twentieth century. It changed our understanding of older physical theories such as Newtonian Physics and led to early Quantum Theory and later the Theory. But the ramifications of special relativity affect everything. Essentially, the theory proposed that distance and time aren't absolute. Now it's time for the third ice cream scoop, and. Special relativity (SR, also known as the special theory of relativity or STR) is the generally accepted and experimentally wellconfirmed physics theory regarding the relationship between space and time. In Albert Einstein's original pedagogical treatment, it is based on two postulates: . The laws of physics are invariant (i. identical) in all inertial systems (nonaccelerating frames of. Einstein's special theory of relativity is well known to provide an accurate description of physical phenomena, providing that the relative velocity v0 does not exceed the speed of light c. The two wellknown formulae for the mass m and energy are 1. 1where m 0 denotes the rest mass, and they apply. If you are a fan of science fiction, then you know that relativity is a fairly common part of the genre. For example, people on Star Trek are always talking about the spacetime continuum, worm holes, time dilations and all sorts of other things that are based on the principle of relativity in one. Einstein's Special Relativity upended our understanding of space, time and energy. While the ideas are subtle, they only require high school algebra, so join this mathbased introduction. For a conceptual introduction check out Space, Time and Einstein. Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity is one of the towering achievements of 20thcentury physics. Published in 1916, it explains that what we perceive as the force of gravity in fact. lecture notes on special relativity. A textbook based on this website is now available from Cambridge University Press. Special relativity is one of the high points of the undergraduate mathematical physics syllabus. Nick Woodhouse writes for those approaching the subject with a background in mathematics: he aims to build on their familiarity with the foundational material and the way of thinking taught in firstyear mathematics courses, but not to assume an unreasonable degree of prior knowledge of traditional. Preface For me, the wonder of special relativity lies in its successful prediction of interesting and very nonintuitive phenomena from simple arguments with simple premises. An essential part of Modern physics is Special Relativity. These applets address some critical points in a student's understanding about this fascinating topic. Most are still under development and many have accompanying lesson plans and ancillary files. For those who want to learn just enough about it so they can solve problems, that is all there is to the theory of relativityit just changes Newtons laws by introducing a correction factor to the mass. Relativity, wideranging physical theories formed by the Germanborn physicist Albert Einstein. With his theories of special relativity (1905) and general relativity (1915), Einstein overthrew many assumptions underlying earlier physical theories, redefining in the process the fundamental concepts of space, time, matter, energy, and gravity. Along with quantum mechanics, relativity is central to. This course introduces the basic ideas and equations of Einstein's Special Theory of Relativity. If you have hoped to understand the physics of Lorentz contraction, time dilation, the twin paradox, and Emc2, you're in the right Knuteson wishes to acknowledge that this course was originally designed and taught by Prof. Chapter 1 Introduction: What is Relativity? U the end of the 19th century it was believed that Newtons three Laws of Motion and the associated ideas about the properties of space and time provided a basis on which the motion of matter could be completely understood. Our idea is to take advantage of these features of special relativity to observe familiar objects in the relativistic cameras different spacetime rest frame. Scientific American, Astronomy at the Speed of Light, 3 July 2018 In 1905, Einstein revealed his ideas on special relativity, using. (April 9, 2012) In the first lecture of the series Leonard Susskind discusses the concepts that will be covered throughout the course. In 1905, while only tw This episode of Crash Course Physics is supported by Prudential. Go to to learn how, if you start saving today, you can continue to enjoy the things you love tomorrow. Simple and straightforward approach. Spacetime Physics, Taylor and Wheeler. An alternative presentation, based entirely on geometric spacetime The book is divided into two sections, an introductory text and a more advanced text. Both texts cover the same topics. Undergraduates might compare their curriculum with the text and study appropriately. Part 1 of the paper that changed the way we understand the universe: Relativity: The Special and General Theory, 1920. The special theory was first proposed in 1905 in Einsteins paper.
-
Related Images: